Complete Guide to Options Trading Terms & Strategies
Learn 100+ Options Strategies

Long Call
A long call is a powerful but risky strategy that benefits from bullish market movements and higher volatility. Use the best options strategy builder with SensaMarket.

Short Call (Naked Call / Uncovered Call)
What is a Short Call? This guide breaks down naked call options strategy, explaining how to profit from a moderately bearish outlook while managing high risk. Track options with the best option trading platform

Long Put
A long put is an options trading strategy used by investors who anticipate a decline in the price of an underlying asset. Learn how to put options to profit with our options trading tracker.

Short Put (Naked put/ uncovered put)
The Short Put Condor is an options strategy designed to profit from a specific range within the underlying asset's price, similar to the Short Call Condor but using put options. Keywords: Short Put Condor Options Strategy

Covered Call
The covered call is a popular options trading strategy revolving around holding a long position in an underlying asset, coupled with the sale of a call option on the same asset. This option is typically employed by investors who are keen on carrying out an additional income stream from stockholdings as a result of premiums received for the calls sold.
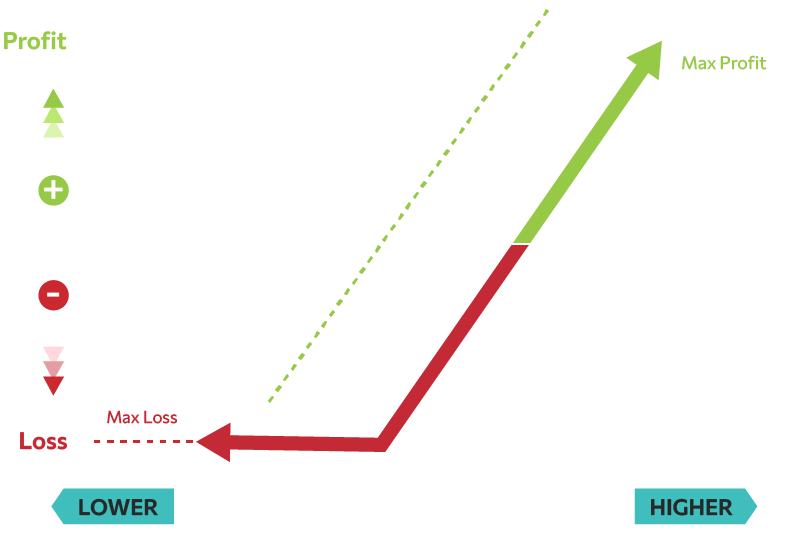
Protective Put / Cash Secured Put
Protective put strategy is commonly used by an investor who wants to hedge against downside risk while maintaining the chance of upside gains. It is buying a put option wherein you own shares, much like insurance against falls in stock prices.

What is Bull Call Spread (Long call spread) Options Trading Strategy?
The Bull Call Spread, also known as a long call spread, is an options trading strategy used when an investor expects a moderate rise in the price of the underlying asset. Learn how to use options strategy builder with SensaMarket.

Bear Put Spread(Long Put spread)
The Bear Put Spread is an options trading strategy utilised when an investor anticipates a moderate decline in the price of the underlying asset. Learn how to use options trading tracker here.

Bear Call Spread (Short Call spread)
A Bear Call Spread is an options trading strategy used when an investor expects a moderate decrease in the price of the underlying asset.Track options with the best option trading platform.

Bull Put Spread (Short Put Spread)
What's a Short Put Spread? This guide breaks down this options strategy, explaining how to profit from a moderately bullish outlook while managing risk. Learn the basic signals, including setup, breakeven, and potential outcomes.

Ratio call spread ( Front Spread with Calls)
The Ratio Call Spread involves buying calls at a lower strike price and selling a greater number of calls at a higher strike price. Track options with the best option trading platform.

Ratio put spread ( Front Spread with Puts)
A Ratio Put Spread or a Front Spread with Puts is a complicated options trading strategy based on a modestly bearish stock outlook but providing some cover against upside risk. In this method, at least one put option at higher strike and more put options at lower strike is sold against a small proportion of put options at the same expiry.

Long Call Condor
Looking for a stock to stay within a specific price range? The Long Call Condor options strategy could be your answer. Track options with the best option trading platform.

Long Put Condor
Learn Long Put Condor options strategy to profit from limited stock price movement. This guide covers setup, breakeven points, maximum profit and loss, risk management, time decay, and ideal market conditions.

Iron Condor
The Iron Condor is a popular options trading strategy used by traders who expect little to no movement in the underlying asset's price. Learn how to use options signals of the underlying asset staying within a certain range.

Short Call Condor
The Short Call Condor is a sophisticated options trading strategy employed to make money from small price movements in the underlying stock. It is similar to the Iron Condor but with only call options with varying strike prices, to make money from low volatility in the underlying stock.

Short Put Condor
The Short Put Condor is an options strategy that is employed to benefit from a specific range in the price of the underlying stock, in a similar way the Short Call Condor is employed but with put options. The strategy involves selling two put options with different strike prices and buying two put options with even higher strike prices, all with the same expiration. It is most suitable when a trader expects little volatility and expects the stock to be in a specific range of prices.

Reverse Iron Condor
The Reverse Iron Condor is an options trading strategy designed to profit from significant movements in the underlying asset's price. Learn how to use options signals with SensaMarket.

Long Straddle
A Long Straddle is a popular options trading strategy used to profit from significant price movements in either direction. Track options with the best option trading platform.

Short Straddle
A Short Straddle is an advanced options trading strategy where a trader sells a call option and a put option simultaneously with the same strike price and date of expiry on the same underlying asset. This strategy is applied when a trader expects the underlying asset's volatility to be low and thereby expects that the stock price will remain more or less in a stable range.

Covered Short Straddle
A Covered Short Straddle is an options strategy that combines risk management with the potential for profit from a stable market. It involves selling a call and a put option with the same strike price and expiration date, while owning the underlying stock in sufficient quantity to cover the call option. This strategy is used when the trader anticipating low volatility feels that the stock price would remain closer to the strike price.

Long Strangle
The Long Strangle is a straightforward options trading strategy designed to profit from significant movements in the underlying asset's price, regardless of the direction. Learn how to use options signals with SensaMarket.

Short Strangle Options Trading Strategy
The Short Strangle is an advanced options trading strategy utilized to profit when the underlying asset's price remains within a specific range. Learn how to use options signals with SensaMarket.

Covered Short Strangle
The Covered Short Strangle is a variation of the basic short strangle, designed to limit risk, selling a call and a put option.Learn how to use options strategy builder with SensaMarket.

Long Call Butterfly
The Long Call Butterfly is an advanced options trading strategy that is used when a trader expects little to no movement in the underlying asset's price. Learn how to use options tracker here.

Long Put Butterfly
The Long Put Butterfly is a sophisticated options trading strategy utilized when an investor anticipates minimal movement in the underlying asset's price. Learn how to use options signals with SensaMarket.

Iron Butterfly
The Iron Butterfly is a neutral options strategy designed for traders who anticipate low volatility in the underlying asset's price. Learn how to read options signals with SensaMarket.

Short Call Butterfly
A short call butterfly is an options trading strategy used by traders who expect minimal or no price action in the underlying asset but are willing to profit from high volatility in the option prices. Generally speaking, this strategy is a reverse of the long call butterfly and it seeks to take advantage of the decay of the premiums for options.

Short Put Butterfly
The Short Put Butterfly is an involved options strategy suitable for traders expecting minimal price movement in the underlying asset but wishing to exploit heightened levels of implied volatility. The strategy is achieved by purchasing and selling put options at three distinct strike prices, but the same expiration date, to exploit theta decay while maintaining defined maximum loss.

Reverse Iron Butterfly
This is an advanced options trading strategy designed to take advantage of huge, sharp moves in the underlying asset, yet have a defined risk profile. This strategy essentially is a long straddle coupled with a short strangle and makes use of both calls and puts to leverage on high volatility situations.

Bull Call Ladder
The Bull Call Ladder, also known as a Long Call Ladder, is the expansion of the Bull Call Spread. In this strategy, a person is both buying and selling different call options at several strike prices. The idea behind this strategy is to create more profit potential than a simple bull call spread could offer, often when the market is modestly bullish but has some allowance for a bigger upside.

Bull Put Ladder
The Bull Put Ladder is an options trading strategy used to enhance the potential profit of a basic bull put spread when a trader expects a moderate rise in the underlying asset's price. Learn how to use options trading tracker here.

Bear Call Ladder (Credit)
The Bear Call Ladder, also referred to as a Short Call Ladder, is an options trading strategy that extends the classic bear call spread to potentially increase profit. Learn how to use options strategy builder with SensaMarket.

Bear Call Ladder (Debit)
The Bear Call Ladder in its typical form results in a credit to the trader's account, as it involves net selling of options—more specifically, selling more calls than are bought. Learn how to use options signals with SensaMarket.

Bear Put Ladder
The Bear Put Ladder is an extension of the basic bear put spread, a more complex strategy. Learn how to use options strategy builder with SensaMarket.

Long Call Ladder – (Bull Call Ladder)
The Long Call Ladder, known also as Bull Call Ladder, is basically an options trading strategy that works as a type of Bull Call Spread with another sold call but at a more elevated strike. This strategy applies when the expectation of the rise in the value of the underlying asset is somewhat moderate but where the trader, at the same time, tries to hedge up against a high surge beyond this point.

Long Call Spread – ( Bull Call Spread)
A long call spread, commonly known as a bull call spread, is an options trading strategy adopted by traders who believe that the underlying asset's price will increase modestly. This strategy is done by purchasing a call option with a lower strike price and selling another call option with a higher strike price at the same time with the same expiration date. This strategy tries to decrease the total cost of the position but limits the potential profit at its maximum level

Long Put Ladder – ( Bear Put Ladder)
The Long Put Ladder, sometimes referred to as the Bear Put Ladder, is a strategy for options trading when a trader has a bearish view of the underlying asset but still wants to limit his upfront cost and maximize potential return in case the value of the underlying moves sharply below. The approach consists of the purchase of put options at a higher strike price along with the selling of more put options at two lower strike prices.

Long Put Spread – ( Bear Put Spread)
The Long Put Spread, also known as a Bear Put Spread, is a simple options trading strategy that is applied when an investor expects a moderate decline in the price of the underlying asset. It involves buying a put option at a higher strike price and simultaneously selling another put option at a lower strike price, both with the same expiration date.

Strip
The Strip strategy is an options trading technique used when an investor expects significant volatility in the underlying asset's price with a stronger bearish bias. Learn how to use options signals with SensaMarket.

Strap
Maximize profit potential with the Strap options strategy. Designed for bullish traders anticipating high volatility, the Strap offers leveraged gains with some downside protection. Learn how the option signals work and if it's right for you.

Long Guts (Guts)
The Long Guts strategy is a lesser-known but effective option trading tactic used when an investor expects significant movement in the underlying asset. Learn how to use options signals with SensaMarket.

Short Guts
The Short Guts strategy is a less common version, the opposite of the Long Guts strategy, involving the sale of in-the-money (ITM) options, both a call and a put. Track options with the best option trading platform.

Collar
A Collar is a form of hedging options strategy in trading whereby an investor owns shares of the underlying stock, yet utilizes both a protective put option and a covered call option. The main purpose of such a strategy is to restrict any losses and to limit the amount of gain possible, thereby it is preferred for investors to be protected from loss due to downtrends but do not sacrifice any upside.

Long Combo
Long combo is known also as synthetic long stock and can be referred to as the imitation of payback of an options trading strategy from owning a stock, although typically at a cheaper cost. In this case, a call option is purchased together with a sell of a put option at similar expiration and also usually of a similar strike. This strategy replicates the effect of a long stock position: it allows both unlimited gains as well as loss potential, both of which mimic the effect of owning the real stock.

Short Combo
The Short Combo strategy, often called a synthetic short stock, is an options trading strategy that replicates the risk and reward profile of selling a stock short. The strategy is done by selling a call option and buying a put option with the same expiration date and usually the same strike price. It is suited for investors who expect a dramatic drop in the price of the underlying stock.

Long Box
The Long Box Spread is an options trading strategy that uses the difference in option price anomalies to exploit these differences. This strategy creates a position that synthetically replicates a risk-free bond. This strategy is accomplished by entering simultaneously into a bull call spread and a bear put spread that have the same strike prices and expiration dates. It is normally used when the net cost of the spreads is less than the spread between their respective strike prices, indicating market price misrepresentation.

Short Box Spread
The Short Box Spread is merely the opposite of the long box spread, where it is applied in options trading to take advantage of over-priced spreads rather than under-priced spreads. It's created by switching the positions from a long box spread, such that you'd sell a bull call spread and a bear put spread. It is an arbitrage strategy with the intention of earning a risk-free profit as it exploits some pricing inefficiency in option spreads.

Call Vertical Spread
The Call Vertical Spread, commonly known as a Bull Call Spread, is a directional trading strategy that bets on a moderate price rise of the underlying asset. This strategy involves buying and selling call options on the same underlying asset with the same expiration date but different strike prices.

Put Vertical Spread
The Put Vertical Spread, popularly known as the Bear Put Spread, is a directional trade which a trader who anticipates that the underlying price of an asset will go moderately lower utilizes. It's essentially the buy of a put option at the higher strike and sell another put option at a lower strike and has the same expiry date.

Calendar Call Spread
The calendar call spread is also known simply as a calendar spread or a time spread, and it involves buying and selling call options of the same strike price but having different expiration dates. This spread is usually made to take advantage of differences in time decay and volatility between the options of the different expiration months.

Calendar Put Spread
Calendar Put Spread, also known as time spread or horizontal put spread, is an options trading strategy that involves the simultaneous purchase of a put option and the sale of another put option with the same strike price but different expiration dates. This strategy is built in such a way as to take advantage of the different rates of time decay between the options and is typically used when the trader anticipates low to moderate volatility from the underlying asset..

Diagonal Call Spread
The Diagonal Call Spread is a rather versatile options trading strategy that brings together the features of both vertical and calendar spreads. It consists of buying a long-term call option at a lower strike price and selling a short-term call option at a higher strike price. This strategy is meant to exploit differences in time decay and strike price for potential profit, particularly in moderately bullish scenarios.

Diagonal Put Spread
The Diagonal Put Spread is an advanced options trading strategy similar to the diagonal call spread but uses put options instead. This is a strategy that involves buying a long-term put option at a higher strike price while selling a short-term put option at a lower strike price. In general, this is used as a strategy to benefit from downward price movements of the underlying asset over time, combined with the benefits of time decay on the sold put.

Iron Butterfly Options Strategy: A Complete Guide for Neutral Market Traders
Learn the Iron Butterfly options strategy with SensaMarket. Explore how the Iron Butterfly option spread works, smart trading tactics, and risk management techniques.
Know the Basics
What Are Options? A Simple Guide to Understanding Options Trading
Options trading explained: Learn about call options, put options, derivatives, strike price, premium, expiration date, and how options can be used for hedging, speculation, and income generation.
Understanding Call and Put Options: A Breakdown of How They Function
Mastering call and put options is the key to successful options trading. This guide breaks down the mechanics of buying and selling calls and puts, and how they can be used in different trading strategies.
Understanding Options: Call and Put Options Explained
Want to learn about options trading? This guide breaks down what options are, how calls and puts work, and the key factors that affect their price. We'll explain buying and selling options, plus the roles of each party involved. Perfect for beginners looking to understand this powerful investment tool.
What are Option Greeks
Understanding Delta: The Key to Options Trading
Delta is a crucial concept in options trading, often considered the most important of the "Greeks" in options analysis. It measures how much the price of an option is expected to move per a one-point change in the price of the underlying asset. Essentially, delta provides a snapshot of the sensitivity of an option's price to movements in its underlying market
Understanding Gamma in Options Trading
Gamma is a critical measure in options trading, representing the rate of change in an option's delta relative to a $1 change in the price of the underlying asset. While delta measures the sensitivity of an option's price to changes in the underlying asset's price, gamma measures the sensitivity of delta itself to those changes. This makes gamma a second-order (acceleration) measure of an option's price sensitivity
Understanding Theta in Options Trading
Theta is a fundamental concept in options trading, representing how the value of an option diminishes over time. This phenomenon, known as time decay, is crucial for traders to understand as it impacts the profitability of options as they approach expiration
Understanding Vega in Options Trading
Vega is a crucial measure in options trading, indicating how sensitive an option's price is to changes in the expected volatility of the underlying asset. It tells us how much the price of an option will change if the implied volatility of the underlying asset increases by one percentage point, assuming all other factors remain constant
Understanding Rho in Options Trading
Rho is a measure of how sensitive an option's price is to changes in interest rates. Specifically, it tells us the amount by which an option's premium is expected to change for each one percentage point change in the risk-free interest rate

What Are Options Greeks? Delta, Theta, Gamma, Vega, Rho Explained with Strike Price Insights
Understand Delta, Theta, Vega, Gamma, and Rho with real examples. Learn how these Greeks impact strike price selection using SensaMarket tools.